What is the Difference Between Fertilizer and Nano Fertilizer?
- Stanislav M.

- Dec 24, 2025
- 4 min read
Updated: Jan 9
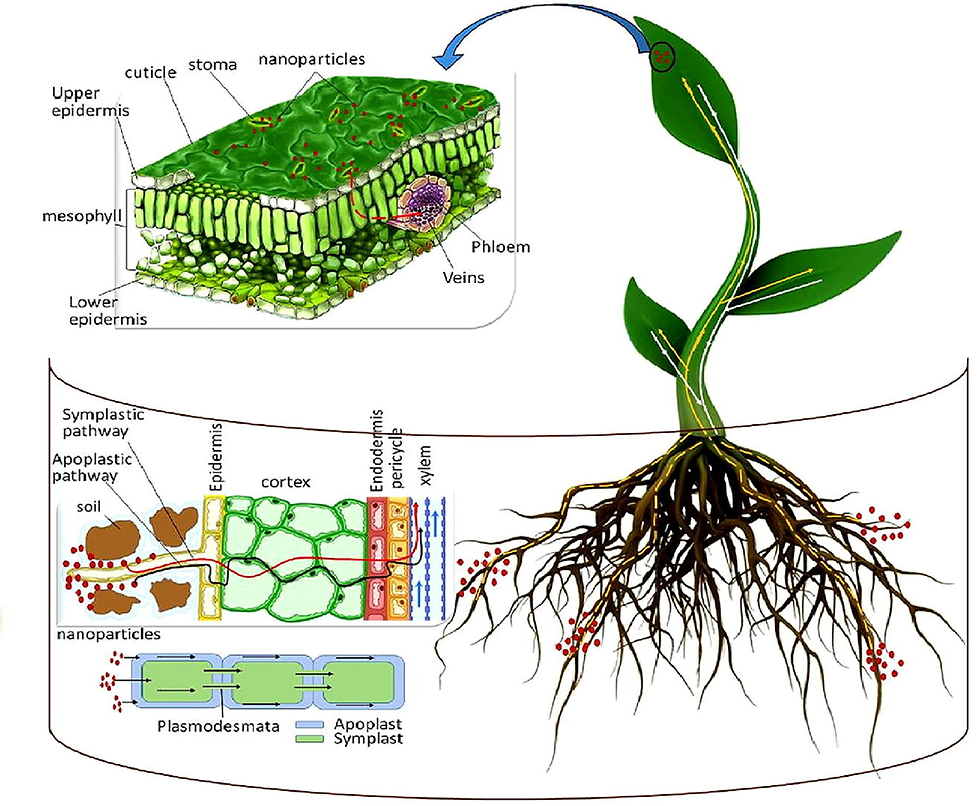
Fertilizers and nano fertilizers both supply essential nutrients to crops, but they differ sharply in particle size, delivery mechanisms, efficiency, and environmental footprint.
Conventional fertilizers release nutrients broadly into soil or on foliage, while nano fertilizers use nanometer-scale carriers to deliver nutrients more precisely, often at much lower doses and with significantly higher nutrient use efficiency. mdpi+2
What Are Conventional Fertilizers?
Conventional (mineral) fertilizers are formulations of nutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), and micronutrients applied in granular or liquid form to soil or foliage.
Once applied, most nutrients dissolve quickly and move in soil solution, where a large fraction can be lost through leaching, runoff, or gaseous losses before plants absorb them.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+2
Typical nutrient use efficiency for conventional nitrogen fertilizers ranges from about 30–50%, meaning roughly half or more of applied N never reaches the crop and instead contributes to water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
What Are Nano Fertilizers?
Nano fertilizers are nutrient formulations engineered at the nanometer scale (1–100 nm) using carriers such as silica, calcium phosphate, or chitosan to encapsulate or bind nutrients. Their small size and high surface area enable controlled or slow release, better contact with plant tissues, and enhanced uptake through roots and foliage, including via stomata and cuticular microchannels. mdpi+2
Reviews and field studies show that nano fertilizers can increase nutrient use efficiency by around 20–30 percentage points compared with conventional fertilizers and often allow similar yields at 30–50% lower application rates.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+2
Key Differences: Fertilizer vs Nano Fertilizer
Particle size and formulation
Conventional fertilizers: Micron–millimeter-scale particles or dissolved ions; nutrients are typically salts like urea, ammonium phosphate, or potassium chloride. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Nano fertilizers: Nanometer-scale particles or nanocarriers, often embedded in biocompatible matrices (e.g., chitosan, amino-acid polymers) that stabilize nutrients in ionic or nano-dispersed form.
Nutrient release and delivery
Conventional fertilizers release nutrients rapidly, often within a few days, leading to high initial availability but also high loss potential.mdpi+1
Nano fertilizers are designed for controlled or synchronized release, maintaining nutrient availability over weeks and better matching plant demand, which improves uptake and reduces losses.agronomyjournals+1
Absorption pathways and mobility
Conventional fertilizers rely mainly on root uptake from soil solution and, for foliar products, surface absorption; translocation may be limited for some nutrients.saskatchewan+1
Nano fertilizers can enter through roots and leaves and move systemically via xylem and phloem thanks to their small size and surface charge, reaching developing tissues (e.g., reproductive organs) more efficiently.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Nutrient use efficiency and yield response
Conventional fertilizers often require higher doses to achieve yield targets because large fractions are lost from the root zone.schoolofpublicpolicy+1
Multiple trials report higher nutrient use efficiency and yield with nano formulations: for example, nano N or nano NPK can maintain or increase yields in crops like potato, maize, rice, and fenugreek at substantially reduced N rates, and nano micronutrients (Zn, Fe, Mn, Mo) improve grain nutrient content and yield relative to chelated or salt forms.iopscience.iop+3
Environmental footprint
Conventional fertilizers are major drivers of nitrate leaching, eutrophication, nitrous oxide emissions, and soil acidification when mismanaged.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Nano fertilizers, by reducing application rates and synchronizing release with uptake, can lower nutrient losses, though their long‑term fate in soil and potential nanoparticle risks still require careful evaluation.mdpi+2
How IndoGulf BioAg Uses Nano Fertilizer Technology
IndoGulf BioAg’s nano fertilizer platform exemplifies these principles through a nano-scale matrix that stabilizes nutrients in charged, colloidal form using amino acids, enzymes, and biopolymer carriers. This design keeps nutrients in plant-available ionic form, supports systemic movement in xylem and phloem, and enables absorption even under drought or salinity stress when conventional uptake is impaired.indogulfbioag+2
Their portfolio includes nano NPK (Anpeekay NPK), nano urea (Nitromax), and a wide suite of nano micronutrients such as Nano Magnesium, Nano Calcium, Nano Boron, and Micromax (multi-micronutrient blend), each formulated to replace substantially larger doses of conventional fertilizers while improving yield and quality.indogulfbioag+2
Practical and Agronomic Implications
For farmers, the choice between conventional and nano fertilizers is increasingly about efficiency and sustainability rather than simply nutrient content. Nano fertilizers tend to have higher unit cost but can reduce total nutrient applied, lower application frequency, and support better yields and produce quality, which can improve profitability over a full season.indogulfbioag+2
In practice, many studies and reviews recommend integrating nano fertilizers with reduced conventional fertilizer doses rather than complete replacement, using nano products to boost nutrient use efficiency and mitigate environmental impacts while leveraging existing fertilizer infrastructure.frontiersin+2
Selected Scientific References
Dimkpa C.O. & Bindraban P.S. 2020. Nano-fertilization as an emerging fertilization technique: Why can modern agriculture benefit from its use? Plants 10, 2. [Open access review on nano fertilizer mechanisms and benefits.]mdpi
Naderi M.R. & Danesh-Shahraki A. 2013. Nanofertilizers and their role in sustainable agriculture. (Discussed in later reviews cited above; overview of efficiency and environmental aspects.)agrifarming+1
Adisa I.O. et al. 2025. The role of nano-fertilizers in sustainable agriculture. (Review of yield and NUE gains and environmental footprint.)pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Chandra S. et al. 2021. Tools for nano-enabled agriculture: fertilizers based on calcium phosphate, silicon and chitosan nanostructures. Agronomy 11, 1239.mdpi
Kumar S. et al. 2021. IFFCO nano fertilizers for sustainable crop production. (Technical report on nano urea performance and N savings.)ureaknowhow
Sandanayake C.L.T. et al. 2022. Yield performances of rice varieties under nano-CuO and nano-ZnO micronutrient fertilizers. Nusantara Bioscience 14: 95–103.smujo
El-Masry M. et al. 2025. Synthesis and characterization of nano-micronutrient fertilizers and their effect on maize under calcareous soil. Scientific Reports.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems 2023. Unveiling the combined effect of nano fertilizers and conventional fertilizers on crop productivity, profitability, and soil well-being.frontiersin
Nano-fertilizers for sustainable African agriculture: A global review of agronomic efficiency and environmental sustainability.mdpi
https://www.indogulfbioag.com/post/nano-fertilizer-nutrient-availability
https://www.agronomyjournals.com/archives/2025/vol8issue7/PartR/8-7-161-123.pdf
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/1225/1/012002
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/1225/1/012024
https://www.indogulfbioag.com/nano-fertilizer/nano-magnesium
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2023.1260178/pdf?isPublishedV2=False
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nanotechnology/articles/10.3389/fnano.2025.1617500/full
https://www.e3s-conferences.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202458801015
http://www.researchjournal.co.in/online/AU/AU%20Spec-5/12_1237-1242_A.pdf
https://www.futurejournals.org/media/eobiwuqx/el-sayed-and-el-taher-31-41.pdf
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/a8f6db8e7d728a1dcd39115ba05e48a98d6ce313
https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5354/10/9/1010/pdf?version=1692960128
https://www.nicheagriculture.com/nano-fertilizers-vs-traditional-fertilizers/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2773111123000219
https://www.ijcmas.com/7-5-2018/Joy%20Kumar%20Dey,%20et%20al.pdf
https://www.indogulfbioag.com/nano-fertilizer/nano-potassium
https://www.indogulfbioag.com/nano-fertilizer/nano-molybdenum
https://www.indogulfbioag.com/post/nano-calcium-university-of-guelph-trials
https://www.indogulfbioag.com/nano-fertilizer/nano-potassium-phosphate



Comments